Nora
 Case Background
Case Background
Name: Nora
Age: 5 months
Sex: Female intact
Breed: Newfoundland
Weight: 28.1 kg
Reason for visit: Murmur evaluation, heard by general veterinarian at wellness appointment.
Age: 5 months
Sex: Female intact
Breed: Newfoundland
Weight: 28.1 kg
Reason for visit: Murmur evaluation, heard by general veterinarian at wellness appointment.
 Clinical History
Clinical History
Attitude/demeanor: Active, alert
Coughing: No cough reported
Respirations: Eupneic, 12 breaths per minute
Exercise intolerance: No change reported
Sleep patterns: Sleeping normally
Weight change: (loss or gain) Gaining weight appropriately for age
Appetite: Normal appetite
Usual diet: Science Diet® Large Breed Puppy
Vomiting: None noted
Diarrhea: None noted
Syncope: None observed
Change in urinary habits: None observed
Change in drinking habits: None observed
Other symptoms or signs: None observed
Coughing: No cough reported
Respirations: Eupneic, 12 breaths per minute
Exercise intolerance: No change reported
Sleep patterns: Sleeping normally
Weight change: (loss or gain) Gaining weight appropriately for age
Appetite: Normal appetite
Usual diet: Science Diet® Large Breed Puppy
Vomiting: None noted
Diarrhea: None noted
Syncope: None observed
Change in urinary habits: None observed
Change in drinking habits: None observed
Other symptoms or signs: None observed
 Physical Exam - General
Physical Exam - General
Body condition: Appropriate body condition, BCS 4/9
Attitude: Bright, alert
Mobility | gait: Normal
Posture: Normal
Hydration: Normal
Body temperature: 100.8 F
Arterial pulse – rate, regularity, intensity: 96 beats/min, regular, slightly hyperkinetic
Rate & respiratory effort: 12 breaths per minute
Mucous membranes – color & CRT: Pink, capillary refill time of 1.5 seconds
Jugular venous pulse & pressure: No pathologic distension, no pulsation
Abdominal palpatation: Unremarkable
Lymph nodes: Normal
Oral cavity: Unremarkable
Other abnormalities: None
Attitude: Bright, alert
Mobility | gait: Normal
Posture: Normal
Hydration: Normal
Body temperature: 100.8 F
Arterial pulse – rate, regularity, intensity: 96 beats/min, regular, slightly hyperkinetic
Rate & respiratory effort: 12 breaths per minute
Mucous membranes – color & CRT: Pink, capillary refill time of 1.5 seconds
Jugular venous pulse & pressure: No pathologic distension, no pulsation
Abdominal palpatation: Unremarkable
Lymph nodes: Normal
Oral cavity: Unremarkable
Other abnormalities: None
 Physical Exam - Auscultation
Physical Exam - Auscultation
Listen to Nora’s heart. (Recommend high-end headphones)
How do you interpret Nora's cardiac auscultation (recorded at the left heart base)?
 Physical Exam - Differential Diagnosis
Physical Exam - Differential Diagnosis
The following are potential diagnoses for you to consider at this time. Based on the history and the physical examination, please indicate the likelihood of each as:
- High (could explain most or all of the signs)
- Possible (less likely to explain most of the signs)
- Unlikely
Subvalvar aortic stenosis
Pulmonary valve stenosis
Patent ductus arteriosus
Functional (innocent) heart murmur
Ventricular septal defect
 Diagnostic Test Selection
Diagnostic Test Selection
Non-invasive blood pressure
CBC with platelet count
Serum biochemical profile (includes electrolytes)
Urinalysis
NT-PROBNP
Thoracocentesis or abdominocentesis for diagnosis or therapy
Thoracic radiographs
Echocardiogram doppler studies
ECG rhythm strip or 6 lead ECG
Ambulatory ECG - holter ECG or event monitor
 Blood Pressure
Blood Pressure
Systolic blood pressure: 102 mmHg, by Doppler on the left forelimb
Diastolic blood pressure: Not available for this case
Mean blood pressure: Not available for this case
Consensus Statements of the American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine (ACVIM) provides the veterinary community with up-to-date information on the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of clinically important animal diseases. In 2018, ACVIM published updated guidelines for the identification, evaluation, and management of systemic hypertension in dogs and cats in the the Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine. Click here to view and download a PDF of the ACVIM consensus statement, guidelines for the identification, evaluation, and management of systemic hypertension in dogs and cats.
Diastolic blood pressure: Not available for this case
Mean blood pressure: Not available for this case
Consensus Statements of the American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine (ACVIM) provides the veterinary community with up-to-date information on the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of clinically important animal diseases. In 2018, ACVIM published updated guidelines for the identification, evaluation, and management of systemic hypertension in dogs and cats in the the Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine. Click here to view and download a PDF of the ACVIM consensus statement, guidelines for the identification, evaluation, and management of systemic hypertension in dogs and cats.
 ECG
ECG
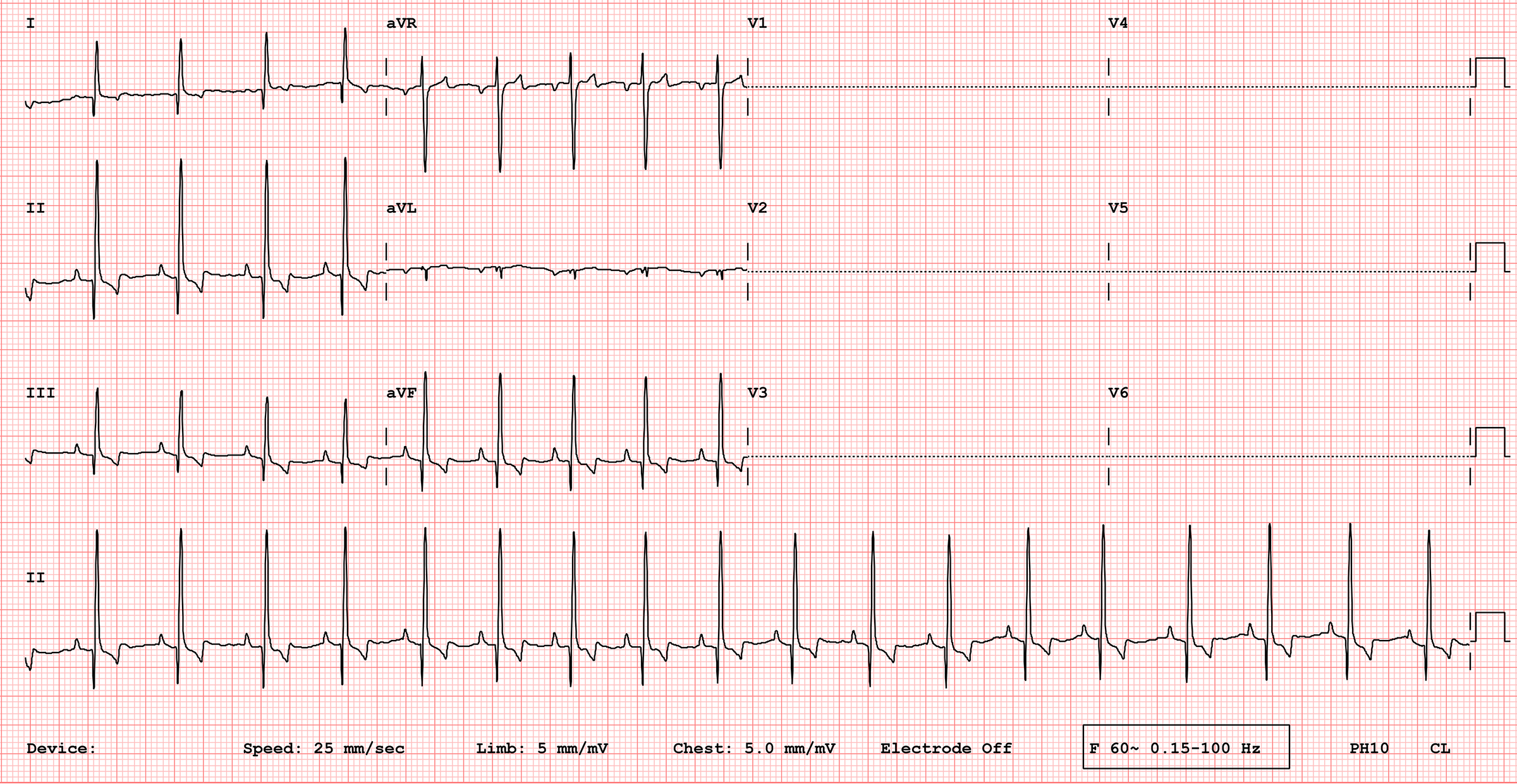
 ECG Interpretation
ECG Interpretation
ECG Interpretation (25 mm/sec, 5 mm/mV): The underlying rhythm is a sinus rhythm. The heart rate averages 110 bpm with slight regular variation (sinus arrhythmia). The mean electrical axis is normal. The R wave amplitude in lead II is 4 mV, which is increased and compatible with left ventricular enlargement. The P wave amplitude is at the upper limit of normal at 0.4mV. All other findings are within normal limits.
 Radiography
Radiography
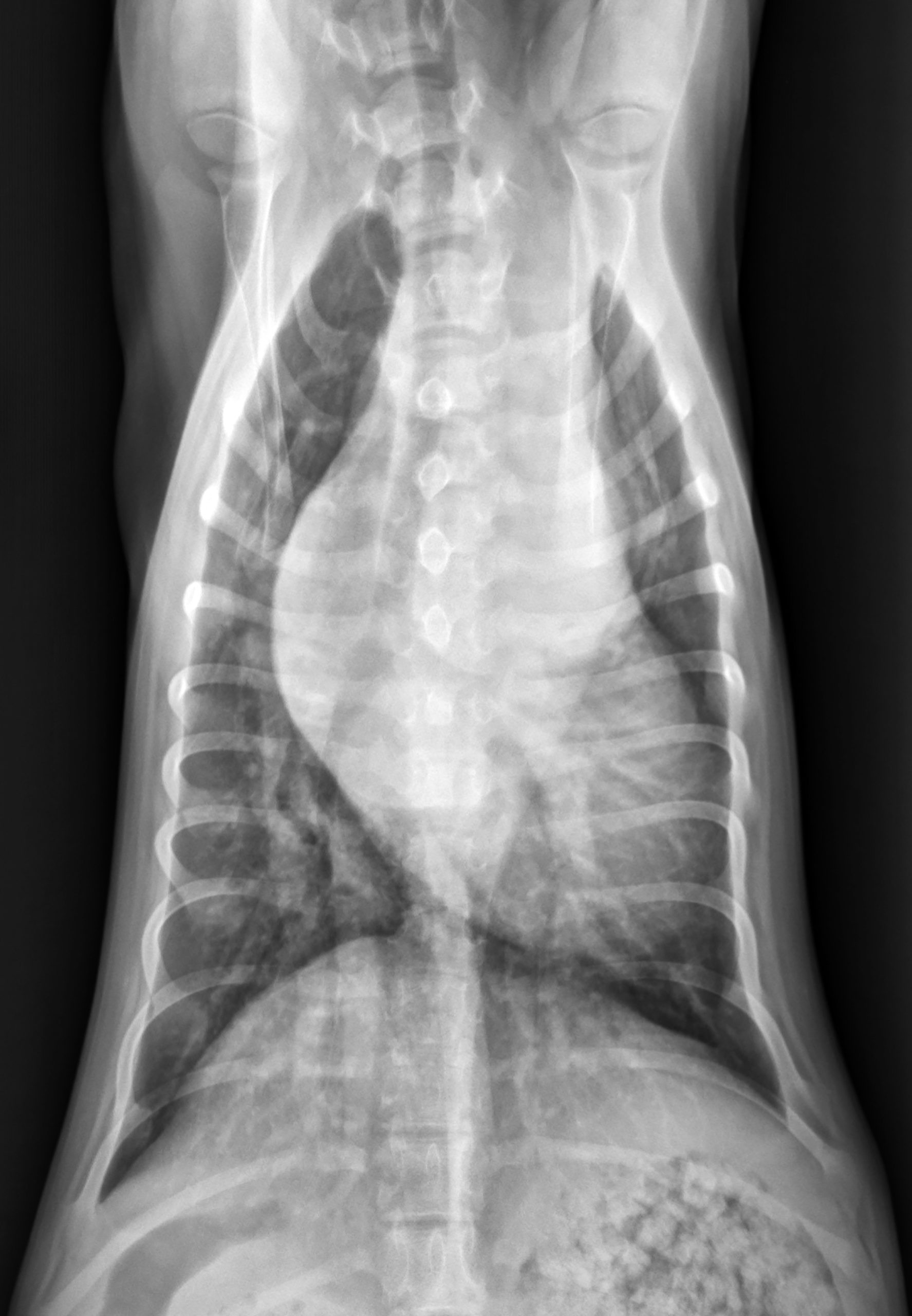
Please review Nora’s thoracic radiographs
Click here for Nora’s radiography viewer (measure VHS and VLAS here) View right lateral radiograph
What is the vertebral heart size (VHS)?
What chambers are enlarged?
 Echocardiography
Echocardiography
 Echocardiographic Interpretation
Echocardiographic Interpretation
LV chamber size and thickness: The left ventricular walls show dilation (eccentric hypertrophy). The wall thickness of the left ventricle is normal.
Left atrial size: Left atrial size appears mildly dilated, but measurements are required to confirm enlargement.
LVIDd & LVIDs: Left ventricular internal dimensions appear increased, consistent with volume overload and eccentric hypertrophy. LV shortening fraction: Nora’s fractional shortening is normal, measuring 32%.
RA, RV and pulmonary artery: The right atrium and right ventricle are normal. The pulmonary valve appears to flutter and is partially closed in systole, related to flow entering the pulmonary trunk.
Doppler results: Color Doppler shows turbulence in the pulmonary trunk with flow entering near the origin of the left pulmonary artery. This flow is continuous, occurring in both systole and diastole.
Left atrial size: Left atrial size appears mildly dilated, but measurements are required to confirm enlargement.
LVIDd & LVIDs: Left ventricular internal dimensions appear increased, consistent with volume overload and eccentric hypertrophy. LV shortening fraction: Nora’s fractional shortening is normal, measuring 32%.
RA, RV and pulmonary artery: The right atrium and right ventricle are normal. The pulmonary valve appears to flutter and is partially closed in systole, related to flow entering the pulmonary trunk.
Doppler results: Color Doppler shows turbulence in the pulmonary trunk with flow entering near the origin of the left pulmonary artery. This flow is continuous, occurring in both systole and diastole.
 Referral
Referral
The echocardiogram shown in this case study was acquired at the cardiologist, following referral from Nora’s general veterinarian. The blood pressure and thoracic radiographs were obtained by the general veterinarian prior to referral.
 Diagnosis & Treatment
Diagnosis & Treatment
You’re ready to form a diagnosis and treatment plan for Nora! Please select your answer to each question below.
What is your diagnosis for Nora?
What treatment(s) would you recommend for Nora?
What surgical options exist for Nora’s condition?
ACTUAL TREATMENT
Procedure: Femoral artery catheterization with device occlusion.
Lifestyle adjustments: None recommended at this time
Diet: No change required
Follow up treatment: Follow-up is recommended with Nora’s general veterinarian in 10-14 days after closure of the duct to remove surgical sutures and perform auscultation. If no murmur is apparent, no further therapy or follow-up is generally required. Had Nora been in heart failure prior to closure of duct, continued management of her heart condition would likely have been required.
 Post Test - CE
Post Test - CE
Please answer the following questions
Which heart chambers are enlarged in a dog with patent arterial duct?
What is the prognosis for an asymptomatic dog with patent ductus arteriosus?
Which physical examination findings are compatible with a patent ductus arteriosus?
The murmur of a patent arterial duct is heard best at the left heart base and with what timing?
The most common congenital heart diseases in the dog are…
 RACE Certification
RACE Certification
RACE Certification
Fill out the following form in order to receive your certificate.